
When you think about Google cache, what comes to mind? That thing you clear out when our computer is running slow? Cache can actually be a useful SEO tool to catch a glimpse of what Google wants you to do.
In this guide, we’ll go through some of the best ways to use Google cache to track competitors and help you potentially rise in the SERPs.
What Is Google Cache?
Google cached pages are HTML backups of the content on a page taken at a certain point in time. This information is stored on a server and can be retrieved later for various purposes.
Periodically, Google crawls sites and takes snapshots of the site at that point. They’ll index so they can refer back later to see what has changed since then.
Google also provides the date and time of that snapshot.
If you’re dealing with underperforming pages or concerns over indexing, or if you’re wondering how often Google is crawling your site, Google cache might be the answer to your problems.
The Three Views for Cached Websites
There are three viewing options for cached sites:
- Full version
- Text-only version
- Source code
Each version is important for different reasons.
The full version of a cached page will provide an exact snapshot of the site when Google passed through. It’ll show the ads, banners, font customization, etc. It’s a replica of the site, with all of the design elements.
Text-only is what Googlebot sees when it crawls the site. It doesn’t see the images, banners, and graphics; all it reads is the text.
This is important for one primary reason: sometimes high-ranking content gets hidden behind media, making it harder for the bot to crawl your site. For this reason, Google uses text-only cache when crawling sites.
If you are looking to obtain useful information from Google cache, you can use both of these views for different purposes.
The full version is essential for seeing updates made to sites. You can look at a competitor’s website that might be outranking you for specific keywords, and you can see what changes they made to their site over time. This applies to media and graphics.
With the text-only version, you can’t do that.
You can use the text-only cache to see what changes were made to the content itself without having to worry about formatting, photos, and videos. This provides a simpler way to look at the text alone, so you don’t miss anything.
To view the page source, right-click and select it from the menu or press CTRL+U on Windows.
This brings up the raw code for the page completely unformatted. Even if you can’t read website code, you might still have a use for this from a marketing and SEO standpoint by understanding what the different tags mean.
How to View Google Cached Pages
If you want to use Google cache to view page versions, there are a few ways you can do this: manually, or with extensions and tools to help you.
We’ll start with the most basic method.
Google Search
Do a Google search for whatever page you want to view. In this case, we’re searching for neilpatel.com.
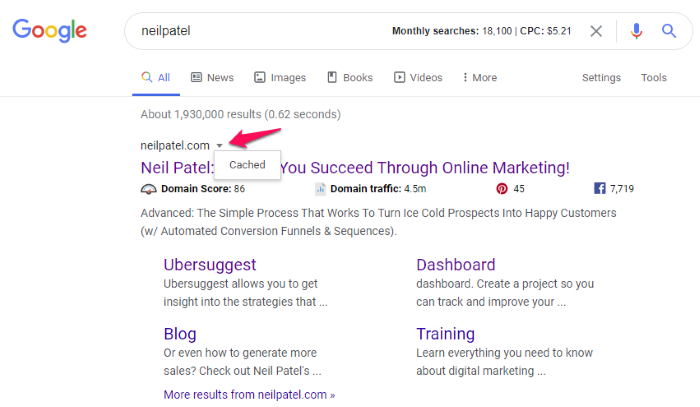
If you look at the URL for the first result, neilpatel.com, you’ll see a small downward-facing arrow to the right of it. Click that, and a menu will appear with a single option: “Cached.”
Click that link to see a cached version of the page. You’ll see a banner at the top with the date and time the snapshot was taken and a link to access the current page.

Another simple method is to type “cache:URL” in the search bar. If you type “cache:neilpatel.com,” it will bring you to the same page we see above.
If you click text-only in the banner at the top, it will eliminate all media, color, graphics, and formatting, and you’ll have a basic snapshot of all the text and links on the site at that time.
Google Cache Checker
Another method for viewing cached pages is the Google Cache Checker. A few different tools are available, but the one I’ve found most accurate and simple is through Small SEO Tools.
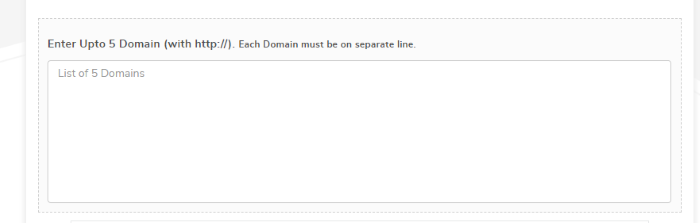
Here you’ll be able to enter up to five domains, and it will provide you with a cache URL and a link you can click to access the cached version of the page.
This method is nearly as simple as using Google, and has the added benefit of letting you do five URLs at once.
Wayback Machine
Archive.org provides a more in-depth picture of a website’s history, and also offers a Chrome extension of its Wayback Machine. Using the Google search method or Google Cache Checker only lets you check the most recent version.
In some cases, the page you want information on was just cached the day before, so you probably wouldn’t get much data out of that.
Wayback Machine provides a ton of information about how many times a site was cached, and they even break it down each day.
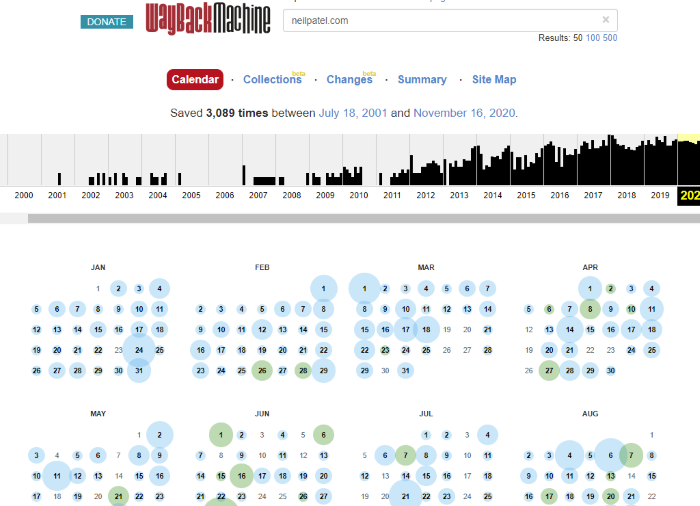
You can click any date and find every single page update that has been made for years. This is a powerful tool that you could use to find small page changes that possibly resulted in increased traffic or ranking.
4 Reasons to Use Google’s Cached Website Feature
You might be wondering, “Why would I want to view old versions of webpages? Isn’t this just for Google to crawl sites, index them, and find errors?”
Well, that’s true, but there’s much more to it than that. There are several uses for Google cache searches, and some can be pretty powerful.
View Changes to Competitors’ Sites
This ninja strategy is a great way to get an idea of what your competitor is doing differently.
Let’s say you’ve been competing for a super challenging keyword for months with a competitor site in the same niche. Thankfully, you’ve been outranking them now for four months straight.
Out of nowhere, they take the number one spot with snippets, and you can’t understand what happened. You didn’t make any changes to your site, there haven’t been any big updates, and everything seems the same for the most part.
What could you do in this situation?
You could use Google cache to see what changes they made.
Check out how many updates they made, what specific changes they made, and compare it to what the page looked like before. You just might find those updates are the reason they’re outranking you.
Check How Frequently Your Site Is Indexed
When Google determines your site is relevant and authoritative based on the keywords you’re using and what audience you’re targeting, Googlebot will index your site more often.
You can use Google cache to see how often they’re indexing your site, and that can help determine if your content is on-par with your target audience and relevant, according to Google.
If you find your site was crawled yesterday, and it updates in a day or two, you could guess the page has high relevance because Google isn’t letting outdated pages sit around.
Google also updates pages that input new content regularly more frequently. If you have a blog you contribute to regularly, Google will start to understand your cadence and will crawl and update the site more frequently.
All of these factors combined could have a positive impact on your rankings.
Use Google Cache to Diagnose Content Errors
If you’re looking at a Google cache of your website, and you’re not thrilled with how frequently they’re indexing your site, you might want to look at your content.
Check out the text-only view and see if there are any errors, fluff, keyword stuffing, or any other no-no’s in the SEO world.
Being able to see older versions of your webpages can help you determine what steps you need to take to make positive changes.
For example, if you updated your site three months ago, and it resulted in a steep climb in the rankings, you might want to make some of those same changes to other pages on your site. With Google cache, you can see what those changes were so you can implement them elsewhere.
See What Information Google Caches
Another great idea is to find competitor sites that are getting cached most often and mimic the same actions on your site. If you notice a top-ranking competitor uploads a small weekly feature to their site, you might want to consider doing the same.
Ideally, you want to model everything the most frequently indexed sites are doing because Google believes their pages are most relevant to the audience, and that same audience applies to your business.
If you can do what they’re doing, Google might think your website also meets the needs of the audience, and you may have a higher chance of increasing in the SERPs.
Limitations of Google Cache
It’s true that everything in SEO has a caveat. Nothing is ever perfect, and we should always take what we see with a grain of salt. While it’s is a great way to get an idea of what your competitors are doing right, it’s not exactly what “Google” sees.
No matter what you do, you’ll never see what Google sees, and we can only try to get as close as possible.
For example, Google uses a web rendering service that uses an outdated version of Chrome, which doesn’t support many of its features.
Rendering exactly what Google sees is impossible without using the same version of the browser they’re using.
The cached pages could also be inaccurate because Google doesn’t always refresh the version each time they index it. Sometimes you might see the same version for weeks or months while small changes are made each time.
It would be easier to implement changes on your site if you could see them on a rolling basis instead of all at once, but that isn’t the case with Google.
Keep in mind a lot of sites use mobile-first indexing, and that can cause error pages. While this isn’t the only reason you would receive an error message, a site change may cause the cache to register improperly.
Finally, sometimes Google doesn’t cache a page at all. Although they index all pages, they don’t cache all of them, so you may never see any changes made to your site or someone else’s. This could lead you to believe Google isn’t even indexing your site.
The moral of the story is, don’t make drastic changes to your site as a result of what you see or learn from the cache. You can use it as a tool for research and guide page improvements, but it shouldn’t be the end-all-be-all.
Conclusion
If this information seems insignificant, we have various other ways to help you increase in the rankings and get more traffic.
Don’t stress too much about this. It’s a great way to see what changes your competitors are making and whether Google thinks your content is relevant, but you don’t have to rely too heavily on it.
There are many ways to increase ranking — this is simply a back pocket strategy for a rainy day.
Have you used Google cache to improve your site? What did you learn from it?
source http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/KISSmetrics/~3/btMzAzIyhbE/
No comments:
Post a Comment